Prevention of cold bridges
What is a cold bridge?
A cold bridge is an area in a building where a gap occurs in the insulation (for example: the roof/wall junction and the wall/floor junction). As these areas will be colder than the main areas there is a greater risk of condensation forming. With condensation comes the added problem of mould.
Windows and door openings
The 1995 edition of the regulations give details for lintels, jabs and sills using lightweight blockwork or insulation to reduce heat losses and ensure that the surface temperature around the openings does not drop to a point where condensation occurs. The metal of pre formed lintels should have 15mm plaster or dry-lining covering it. The following diagrams are examples of typical methods of complying with the requirement - other methods may be acceptable.
Reducing bridging around openings
Insulating blockwork
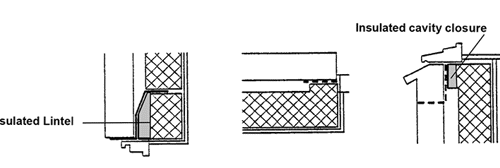
Full cavity fill
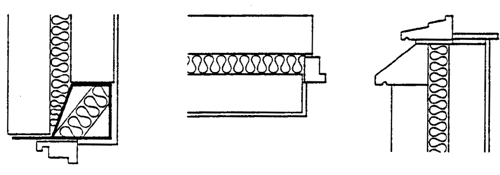
The thermal conductivity of the blockwork should not exceed 0.16W/mK (for example: autoclaved aerated concrete) and the frame should overlap the blockwork by at least 30mm for dry-lying or 55mm for lightweight plaster.
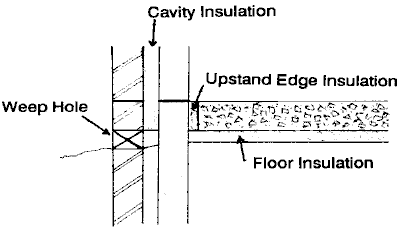
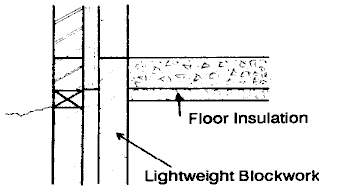
Floors
Where the continuity of the insulation between the floor and external wall/internal load-bearing walls is broken a thermal bridge is formed and there is a risk of condensation forming. To avoid this several methods are acceptable:
- Start the cavity insulation below the DPC level and to the least the same level as the base of the floor slab.
- Use insulating blockwork for the inner leaf of a cavity wall below DPC if structurally sound and suitable for the ground conditions
- Use a vertical strip of insulation at the perimeter of the slab to provide an overlap with the cavity insulation or to link with the internal wall insulation.
- For internal walls use vertical insulation (1m from external wall) to use insulation blocks below DPC.
Floor details
Roofs
Flat roofs
Ensure that the ceiling insulation is carried over the wall - plate to meet the wall insulation. A 50mm air space must be maintained over the flat roof insulation and a 25mm gap provided at opposite sides of the roof.
Flat roof details
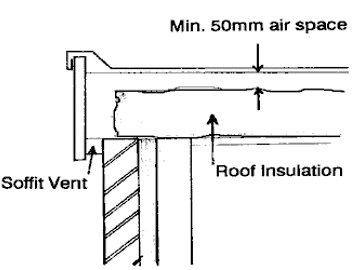
Pitched roofs
Carry the roof insulation down to meet the wall insulation. In order to maintain a 50mm air space at the eaves position use a purpose made spacer to leave a space under the sarking felt.
Pitched roof details
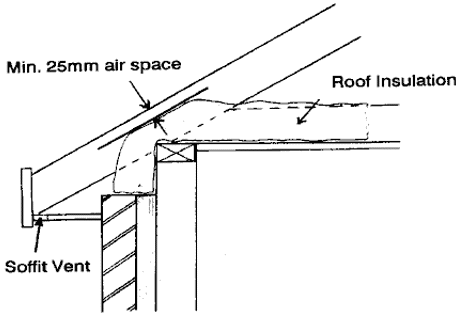
Pitched roofs
Carry the roof insulation down to meet the wall insulation. In order to maintain a 50mm air space at the eaves position use a purpose made spacer to leave a space under the sarking felt.
General Items
Can I leave out the sand blinding under the floor insulation?
No. This leaves out hollows under the insulation and prevents solid insulations breaking up.
Can I use bricks or cinder blocks to close the cavity?
No. They are too dense and will lead to condensation. Use lightweight block or insulation.
Can I completely fill a roof void with insulation
Normally no. Unless 50mm air space is left over the insulation, condensation may form on the timber. There are special forms of construction which may allow you to do this but please contact the Building Control Service for specific advice.